Sarcopenia, a disease long associated with aging and the elderly, is now been determined to really develop earlier in life!
It leads to physical disability, a decrease in quality of life, and an increased mortality risk.1 It affects 10 %–16 % of the elderly worldwide.
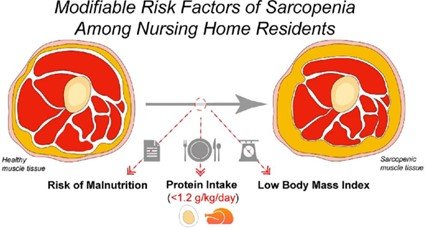
Fig: Illustration of Healthy Muscle tissue compared with that of a sarcopenic patient. Source: Nutr Res. 2022 May:101:14-22.
BREAKING DOWN SARCOPENIA
According to research, it is primarily influenced by the:
- Lifestyle Behaviour: Decreased exercise due to sedentary lifestyles, and smoking may increase the risks of acquiring to sarcopenia.5, 3
- Low body mass index and Daily protein intake: It is estimated that less than 1.2 g/kg of daily protein intake is associated with a higher risk of sarcopenia.4
- Aging Factor & Metabolical Changes: Aging-related changes in mitochondria, apoptosis, and the angiotensin system decline neuromuscular junctions and production of hormones.3, 7
- Gender Factor: Sarcopenia is linked to a higher risk of death in older women.4
- Health status: Chronic conditions, like rheumatism, cancer, and CHD reduce skeletal muscle mass due to high inflammatory cytokines that may induce sarcopenia.3
When there are no clear-cut causes other than aging itself it is identified as Primary sarcopenia. When other variables, such as systemic illnesses like organ failure or cancer, become obvious in addition to aging, it is categorized as Secondary sarcopenia. 2
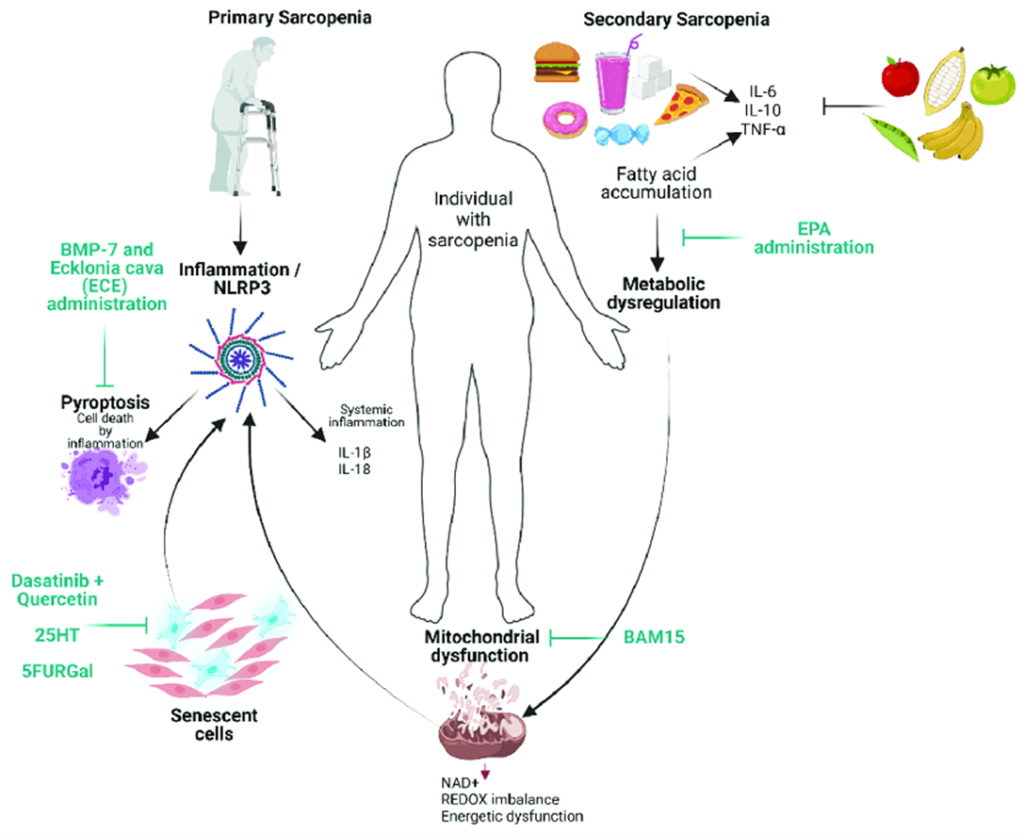
Fig: Factors involved in primary and secondary sarcopenia. Source: Cells 2022, 11, 2359
Consequences of this muscle murderer are associated with a high risk of cognitive impairment, osteoporosis, falls, fractures, functional decline, hospitalization, metabolic syndromes, diabetes, non-alcoholic liver disease, liver fibrosis, hypertension, depression, Dysphagia (swallowing difficulties) 7
Unraveling the Convention on Diagnosis!
Delaying or skipping treatment for sarcopenia may reduce the likelihood of having a good quality of life, more treatment-related issues, and more healthcare expenses.
As per AWGS (Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia) by evaluating muscle strength, physical performance, and skeletal muscle mass by assessing, Handgrip strength, Calf circumference, Walking speed, Difficultness rising from a chair, etc., can help detect sarcopenia efficiently. 2, 5
When Are You At Risk?
After the age of 30, adults lose 3-8% of their muscle mass per decade. Sarcopenia most commonly affects people ages 60 and older. The rates increase with age. 6, 7
Researchers have evidence that skeletal muscle mass and strength go down linearly from the fourth decade of your life onward, with up to 50% of mass being lost by the eighth decade of life. 6
FINAL THOUGHTS
Research has shown the development of sarcopenia takes a long time and does not appear on short notice. So considering the factors that may give rise to muscle disorders like sarcopenia, people need to have an active lifestyle indulging in a workout routine paired with proper nutrition is important to watch out for stealthy muscle murderers like sarcopenia.
REFERENCES
- Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8: 739251.
- Sci Rep. 2020; 10: 19551. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7658996/
- Cells 2022, 11(15), 2359; https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11152359
- Nutr Res. 2022 May:101:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2022.02.002. Epub 2022 Feb 18.
- Arch Public Health 78, 113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13690-020-00498-9
- Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012 Nov; 24(6): 623–627. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328358d59b
7.Metabolism. 2023 Jul:144:155533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155533

